DisplayPort vs. HDMI vs. VGA: A Comparative Analysis
1. Introduction
Purpose and Importance of Display Interfaces
Display interfaces are crucial for connecting video sources to display devices such as monitors, televisions, and projectors. They determine the quality of the visual and audio output and play a vital role in various applications, from home entertainment to professional work.
Overview of DisplayPort, HDMI, and VGA
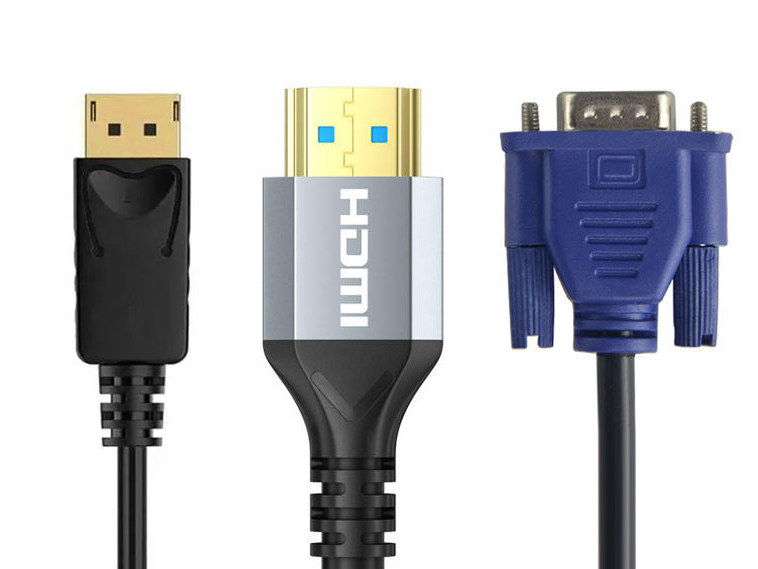
- DisplayPort: A digital display interface primarily used for connecting computers to monitors. It supports high resolutions and refresh rates, as well as audio transmission.
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface): A widely-used digital interface for transmitting both video and audio signals. Commonly found in consumer electronics such as TVs, gaming consoles, and media players.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array): An older analog display interface used for connecting computers to monitors and projectors. While largely replaced by digital interfaces, it is still used in some legacy systems.
2. Technical Specifications
DisplayPort
- Versions: DisplayPort 1.0 to 2.0
- Maximum Resolution: Up to 8K (7680 x 4320) at 60Hz (DisplayPort 1.4) and 10K at 60Hz (DisplayPort 2.0)
- Maximum Bandwidth: Up to 80 Gbps (DisplayPort 2.0)
- Audio Support: Yes, supports multi-channel audio
HDMI
- Versions: HDMI 1.0 to 2.1
- Maximum Resolution: Up to 10K (10240 x 4320) at 120Hz (HDMI 2.1)
- Maximum Bandwidth: Up to 48 Gbps (HDMI 2.1)
- Audio Support: Yes, supports multi-channel audio, including Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio
VGA
- Versions: Standard VGA, SVGA, XGA, etc.
- Maximum Resolution: Typically up to 1920 x 1200 at 60Hz
- Maximum Bandwidth: Limited by analog signal quality
- Audio Support: No, video-only interface
3. Signal Type and Quality
Digital vs. Analog
- DisplayPort and HDMI: Both transmit digital signals, which ensure high-quality, interference-free video and audio transmission.
- VGA: Transmits analog signals, which are more susceptible to interference and signal degradation, especially over longer distances.
Resolution and Refresh Rates
- DisplayPort: Supports higher resolutions and refresh rates compared to HDMI and VGA, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as gaming and professional graphics work.
- HDMI: Supports high resolutions and refresh rates, suitable for most consumer electronics and home entertainment systems.
- VGA: Limited to lower resolutions and refresh rates, making it less suitable for modern high-definition displays.
Audio Transmission
- DisplayPort and HDMI: Both support audio transmission, allowing a single cable to carry both video and audio signals.
- VGA: Does not support audio transmission, requiring separate cables for audio.
4. Connector Types and Compatibility
DisplayPort Connectors
- Standard DisplayPort: Larger connector, commonly used in desktop computers and monitors.
- Mini DisplayPort: Smaller connector, often found in laptops and some tablets.
HDMI Connectors
- Standard HDMI (Type A): Most common connector, used in TVs, monitors, and media players.
- Mini HDMI (Type C): Smaller connector, used in some cameras and portable devices.
- Micro HDMI (Type D): Even smaller connector, used in very compact devices.
VGA Connectors
- Standard VGA (DE-15): 15-pin connector, used in older computers, monitors, and projectors.
5. Use Cases and Applications
Home Entertainment
- HDMI: Dominates in home entertainment systems, connecting TVs, gaming consoles, Blu-ray players, and streaming devices.
- DisplayPort: Less common but used in some high-end home theater setups and gaming monitors.
- VGA: Rarely used in modern home entertainment systems, primarily found in older equipment.
Professional and Creative Work
- DisplayPort: Preferred for professional graphics work, video editing, and multi-monitor setups due to its high resolution and refresh rate support.
- HDMI: Used in professional environments for presentations, conferencing, and connecting various multimedia devices.
- VGA: Still found in some legacy professional equipment and older projectors.
Gaming
- DisplayPort: Favored by gamers for its support of high resolutions, refresh rates, and adaptive sync technologies (e.g., G-Sync, FreeSync).
- HDMI: Widely used in gaming consoles and gaming monitors, supporting high-definition video and audio.
- VGA: Not suitable for modern gaming due to its limitations in resolution and refresh rates.
Industrial and Legacy Systems
- DisplayPort and HDMI: Increasingly used in industrial applications for high-resolution displays and modern equipment.
- VGA: Still prevalent in legacy systems and older industrial equipment, where upgrading to digital interfaces may not be feasible.
6. Advantages and Limitations
DisplayPort
- Advantages: High resolutions and refresh rates, support for multiple monitors, audio transmission, and adaptive sync technologies.
- Limitations: Less common in consumer electronics compared to HDMI.
HDMI
- Advantages: Widespread use, high resolutions and refresh rates, audio transmission, and support for advanced audio formats.
- Limitations: Slightly lower maximum resolutions and refresh rates compared to DisplayPort.
VGA
- Advantages: Compatibility with older equipment, widely available in legacy systems.
- Limitations: Lower resolution and refresh rate support, analog signal susceptible to interference, no audio transmission.
7. Future Prospects
Technological Advancements
- DisplayPort: Continued development with higher bandwidth and support for emerging display technologies.
- HDMI: Ongoing updates to support higher resolutions, refresh rates, and advanced audio and video features.
- VGA: Gradual phase-out as digital interfaces become more prevalent.
Emerging Standards
- DisplayPort 2.0: Promises significant improvements in bandwidth and support for higher resolutions and refresh rates.
- HDMI 2.1: Expands capabilities with higher bandwidth, support for 10K resolution, and enhanced audio and video features.
8. Conclusion
DisplayPort, HDMI, and VGA each have their unique advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications. DisplayPort excels in high-performance and professional settings, HDMI is the go-to choice for home entertainment and consumer electronics, and VGA remains relevant in legacy and industrial systems. Understanding the differences between these interfaces helps users make informed decisions based on their specific needs and requirements.