In today’s digital age, where we rely on an array of devices to get work done, stay entertained, and communicate, having sufficient ports on our computers is crucial. This is where a USB 3.0 hub comes into play. But what exactly is a USB 3.0 hub, and why might you need one? Let’s delve in.
Definition and Basics
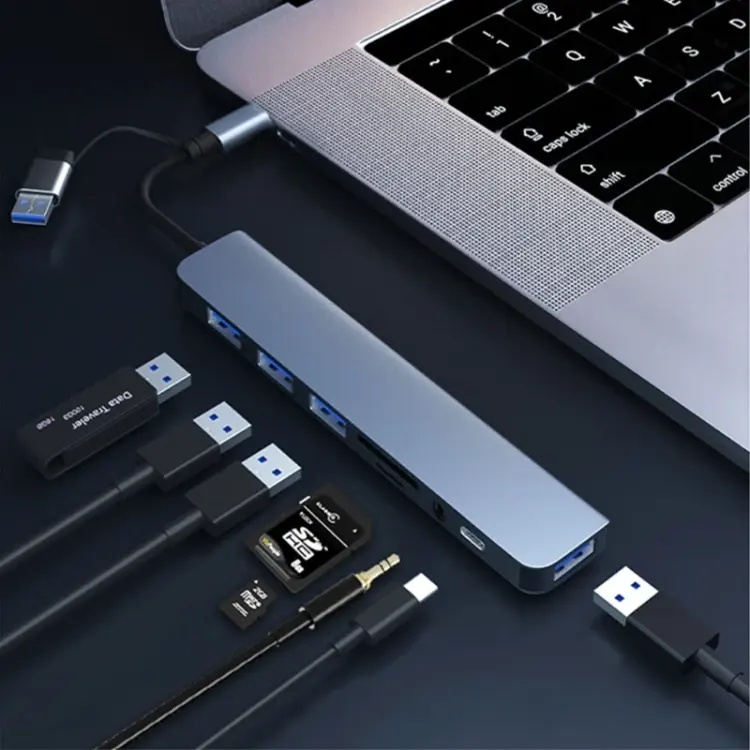
A USB 3.0 hub is a device that expands the number of USB ports on your computer. It acts as a central connection point, allowing you to plug in multiple USB – enabled devices into a single USB port on your computer. For example, if your laptop only has two USB ports but you need to connect a mouse, keyboard, external hard drive, and a printer, a USB 3.0 hub can solve this problem by providing additional ports.
How Does It Work?
The USB 3.0 hub functions by receiving data from the computer through its upstream port (the port that connects to the computer) and then distributing that data to the multiple downstream ports (the ports where you connect your devices). It manages the communication between the computer and all the connected devices, ensuring that data is transferred accurately and efficiently. USB 3.0 hubs use a high – speed protocol to transfer data, which we’ll explore in more detail in the next section.
Advantages of USB 3.0 Hubs
Lightning – Fast Data Transfer Speeds
USB 2.0 vs. USB 3.0: Key Performance Comparison
Feature | USB 2.0 | USB 3.0 |
Max Data Transfer Speed | 480 Mbps | 5 Gbps (≈10x faster) |
1GB File Transfer Time | 15–20 seconds | 1–2 seconds |
Power Output | Up to 500 mA | Up to 900 mA |
Ideal Use Cases | Basic peripherals (mouse, keyboard) | High-speed devices (external SSD, 4K cameras) |
One of the most significant advantages of a USB 3.0 hub is its data transfer speed. USB 3.0 offers data transfer rates of up to 5 Gbps (gigabits per second), which is approximately ten times faster than its predecessor, USB 2.0. To put this into perspective, transferring a large 1GB file with USB 2.0 might take around 15 – 20 seconds, while with USB 3.0, it can be done in just 1 – 2 seconds. This speed is incredibly beneficial for tasks such as transferring large video files, backing up data to an external hard drive, or syncing data – intensive devices.
Enhanced Power Supply
USB 3.0 hubs are designed to supply more power to connected devices compared to USB 2.0 hubs. As shown in the table above, USB 3.0 delivers up to 900 mA of power, which means devices like external hard drives (which often require 600–800 mA) can be directly powered through the hub without a separate adapter. Additionally, it allows for faster charging of smartphones and tablets—reducing charge time by 20–30% compared to USB 2.0 hubs.
Expanded Connectivity Options
With the increasing number of USB – based peripherals available, from keyboards and mice to printers, scanners, and cameras, the built – in USB ports on our computers often fall short. A USB 3.0 hub can extend a single USB port into multiple ports, typically ranging from 4 – 10 ports depending on the model. This enables you to connect all your devices simultaneously without constantly unplugging and replugging them.
Backward Compatibility
USB 3.0 hubs are backward – compatible with USB 2.0 and USB 1.1 devices. This means that you can still use your older peripherals with a USB 3.0 hub. However, when a USB 2.0 or USB 1.1 device is connected to a USB 3.0 hub, the data transfer speed will be limited to the capabilities of the older device.
Types of USB 3.0 Hubs
Powered vs. Bus – Powered Hubs
Powered vs. Bus – Powered USB 3.0 Hubs: Comparison
Factor | Powered USB 3.0 Hub | Bus – Powered USB 3.0 Hub |
Power Source | External AC adapter | Draws power from computer’s USB port |
Power Output | Up to 2.4A per port (varies by model) | Limited to computer’s USB output (usually 900 mA total) |
Portability | Bulkier (requires adapter) | Compact, lightweight (no cables) |
Ideal Devices | External SSDs, multiple hard drives, printers | Mouse, keyboard, flash drives, smartphones |
Best For | Desktop setups, power – hungry devices | Laptops, on – the – go use |
Price Range | \(25–\)60 | \(10–\)30 |
Multi – Function Hubs
Common Multi – Function USB 3.0 Hub Types
Hub Type | Key Additional Features | Target Users |
Ethernet – Enabled Hub | 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet port | Laptop users needing wired internet (e.g., travel, weak Wi – Fi) |
Card Reader Hub | SD/CF/XQD card slots | Photographers, videographers (quickly access camera media) |
USB – C Combo Hub | 1–2 USB – C ports (for charging/l data) | MacBook/iPad users (mix of USB – A and USB – C devices) |
Charging – Focused Hub | 2–4 fast – charge ports (18W+) | Users with multiple devices (phones, tablets, wireless earbuds) |
Choosing the Right USB 3.0 Hub
USB 3.0 Hub Buying Guide: Key Factors
Consideration | Questions to Ask Yourself | Recommended Option |
Number of Ports | How many devices do I need to connect at once? | 4 ports = basic use (mouse, keyboard, flash drive); 7+ ports = multiple high – speed devices |
Power Needs | Do I use power – hungry devices (e.g., external SSD)? | Powered hub (if yes); Bus – powered (if only basic peripherals) |
Portability | Will I use the hub with a laptop on the go? | Bus – powered or compact multi – function hub (no adapter) |
Extra Features | Do I need Ethernet, card slots, or USB – C? | Multi – function hub (match features to your use case) |
Budget | How much am I willing to spend? | \(10–\)30 = basic bus – powered; \(25–\)60 = powered/multi – function |