Different Types of USB cables
Introduction
Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology has revolutionized the way we connect and interact with digital devices. Since its inception, USB has undergone several iterations, resulting in a variety of cable types such as USB-A, USB-B, Micro-USB, USB-C, and Lightning. This paper explores the reasons behind the existence of different types of USB cables, highlighting their technical specifications, applications, and the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
Technical Specifications
Overview of USB Standards
USB standards have evolved significantly, with each new version introducing enhancements in data transfer rates, power delivery, and connector design. Key standards include USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, and USB 3.2. USB 4 is the latest iteration, offering data transfer rates of up to 40 Gbps and improved power delivery capabilities.
Key Differences Between USB Types
The different types of USB cables vary in terms of connector design, data transfer rates, and power delivery capabilities. For instance, USB-A and USB-B connectors are larger and primarily used in older devices, while Micro-USB and USB-C connectors are smaller and more versatile. The Lightning connector, developed by Apple, is unique to Apple devices and offers a proprietary design with specific features.
Construction and Materials
High-quality USB cables are constructed using materials that minimize signal degradation and electromagnetic interference. Shielding, gold-plated connectors, and high-purity copper conductors are common features that enhance performance and durability. The cable length also plays a critical role in maintaining signal integrity, with longer cables requiring more robust construction to prevent signal loss.
Types of USB Cables
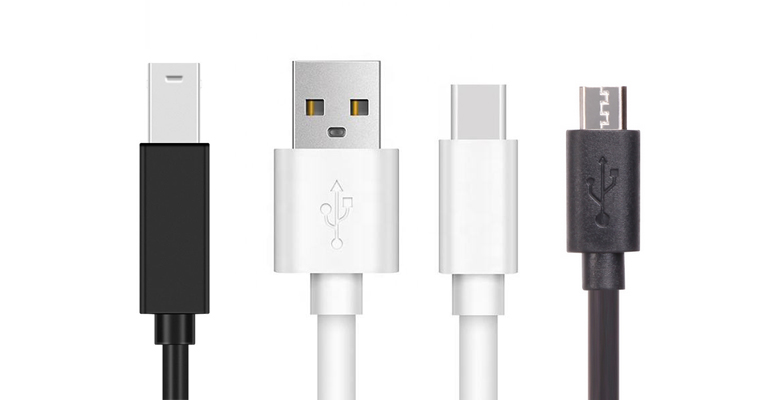
USB-A
USB-A is the original USB connector type, characterized by its rectangular shape. It is commonly used in computers, chargers, and peripherals. USB-A connectors support various USB standards, including USB 1.1, USB 2.0, and USB 3.0.
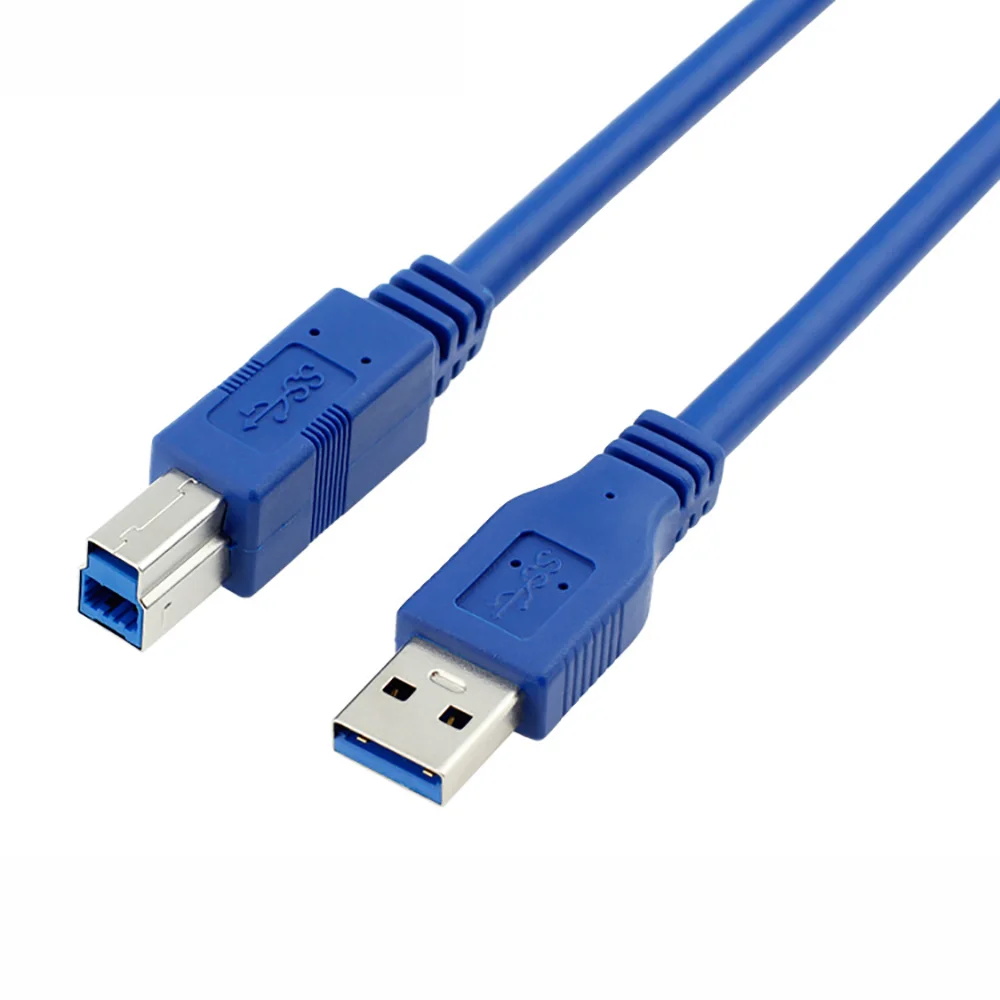
USB-B
USB-B connectors are square-shaped and typically used in printers, scanners, and other peripheral devices. They are less common in consumer electronics but are still used in some older devices.
Micro-USB
Micro-USB connectors are smaller and more compact than USB-A and USB-B connectors. They are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. Micro-USB connectors support USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 standards.
USB-C
USB-C is the latest USB connector type, characterized by its reversible design and versatility. It supports higher data transfer rates and power delivery capabilities, making it suitable for a wide range of devices, including laptops, smartphones, and tablets. USB-C connectors support USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and USB 4 standards.
Lightning
The Lightning connector is a proprietary design developed by Apple for its devices. It is characterized by its small size and reversible design. Lightning connectors support high-speed data transfer and power delivery, making them suitable for iPhones, iPads, and other Apple devices.
Reasons for Different Types
Technological Advancements
As technology has advanced, the need for faster data transfer rates and higher power delivery capabilities has led to the development of new USB standards and connector types. For example, USB-C was introduced to support higher data transfer rates and power delivery capabilities, making it suitable for modern devices .
Device Compatibility and Design
Different types of USB connectors are designed to be compatible with specific devices and use cases. For example, Micro-USB connectors are commonly used in portable devices due to their small size, while USB-A connectors are used in computers and chargers. The Lightning connector was developed by Apple to provide a proprietary solution for its devices.
Power Delivery and Data Transfer Requirements
The power delivery and data transfer requirements of different devices also influence the design of USB connectors. For example, USB-C connectors support higher power delivery capabilities, making them suitable for charging laptops and other high-power devices. Similarly, Lightning connectors support high-speed data transfer and power delivery for Apple devices.
Applications and Use Cases
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics space, USB cables use to connect a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and peripherals. This allows users to charge their devices, transfer data, and connect to other devices and accessories.
Industrial and Professional Applications
USB cables use in industrial and professional applications, such as digital signage, video conferencing, control rooms, and medical imaging.These environments require reliable and high-quality connections to ensure seamless operation and clear communication.
Specialized Use Cases
Specialized use cases for USB cables include applications in gaming, virtual reality, and professional video production. These environments require high-speed data transfer and reliable connections to ensure optimal performance and user experience.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pros and Cons of Each Type
Each type of USB connector has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, USB-A connectors are widely compatible and easy to use, but they are larger and less versatile than USB-C connectors. Micro-USB connectors are compact and suitable for portable devices, but they do not support the same data transfer rates and power delivery capabilities as USB-C connectors. Lightning connectors offer a proprietary solution for Apple devices, but they are not compatible with non-Apple devices.
Performance Metrics and Benchmarks
Performance metrics for USB cables include data transfer rates, power delivery capabilities, and signal integrity. Benchmarks have shown that USB-C connectors offer the highest data transfer rates and power delivery capabilities, making them suitable for modern devices and applications.
Future Trends and Developments
Emerging USB Standards
The future of USB technology is likely to see further advancements in data transfer rates, power delivery capabilities, and connector design. USB 4 is the latest standard, offering data transfer rates of up to 40 Gbps and improved power delivery capabilities. Future standards may introduce even higher performance metrics and new features to meet the growing demands of modern devices.
Innovations in Cable Technology
Innovations in cable technology, such as the use of higher-quality materials, improved shielding, and advanced signal processing chips, have significantly enhanced the performance of USB cables. These advancements ensure that users can enjoy high-speed data transfer and reliable connectivity with minimal latency and interference.
Conclusion
The existence of different types of USB cables, such as USB-A, USB-B, Micro-USB, USB-C, and Lightning, is driven by technological advancements, device compatibility and design, and power delivery and data transfer requirements. Each type of USB connector offers its own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for specific use cases and applications. As technology continues to evolve, further advancements in USB standards and innovations in cable technology will ensure that USB cables remain an essential component in the world of digital connectivity.